
Lost Women of Science
Lost Women of ScienceFor every Marie Curie or Rosalind Franklin whose story has been told, hundreds of female scientists remain unknown to the public at large. In this series, we illuminate the lives and work of a diverse array of groundbreaking scientists who, because of time, place and gender, have gone largely unrecognized. Each season we focus on a different scientist, putting her narrative into context, explaining not just the science but also the social and historical conditions in which she lived and worked. We also bring these stories to the present, painting a full picture of how her work endures.
For every Marie Curie or Rosalind Franklin whose story has been told, hundreds of female scientists remain unknown to the public at large. In this series, we illuminate the lives and work of a diverse array of groundbreaking scientists who, because of time, place and gender, have gone largely unrecognized. Each season we focus on a different scientist, putting her narrative into context, explaining not just the science but also the social and historical conditions in which she lived and worked. We also bring these stories to the present, painting a full picture of how her work endures.

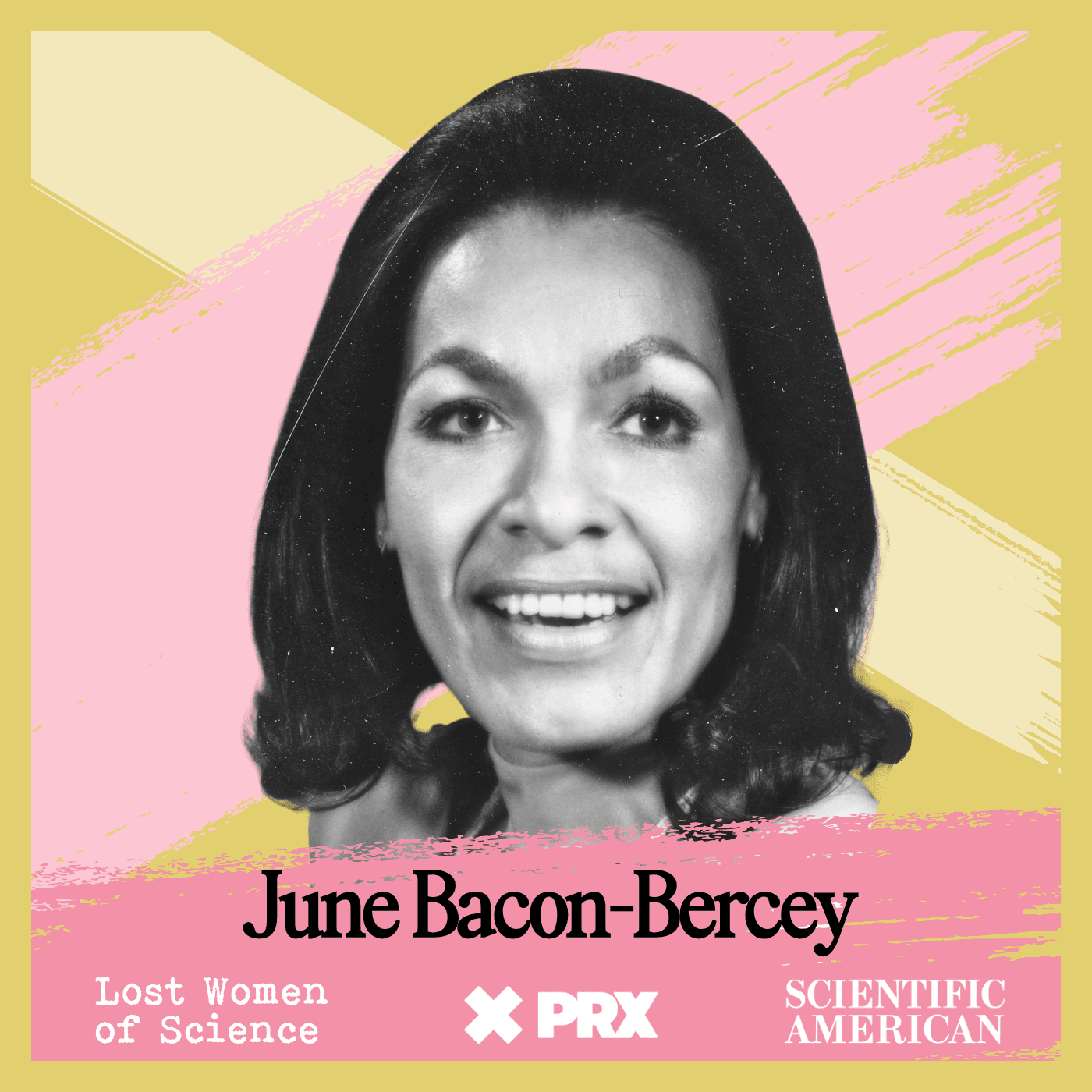




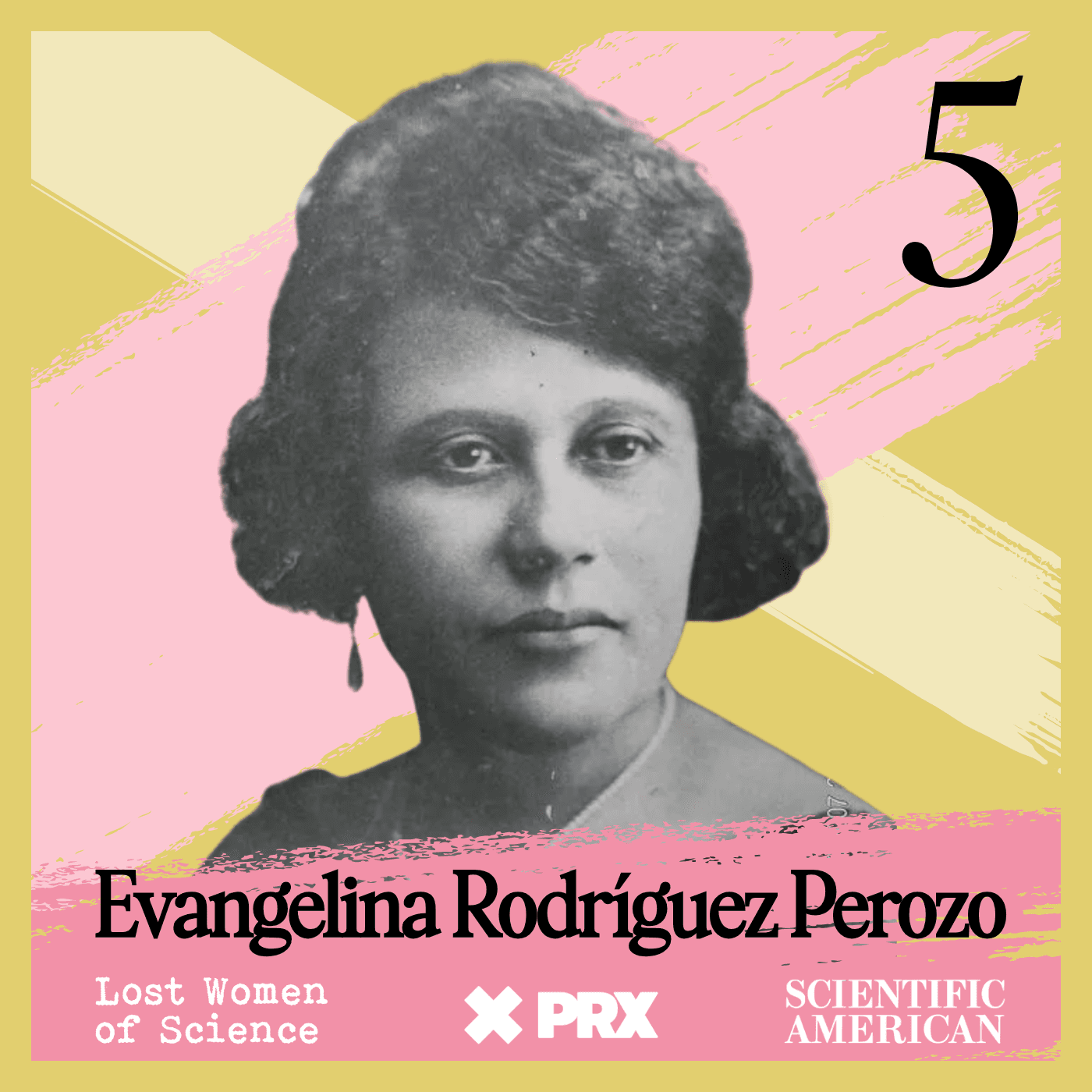
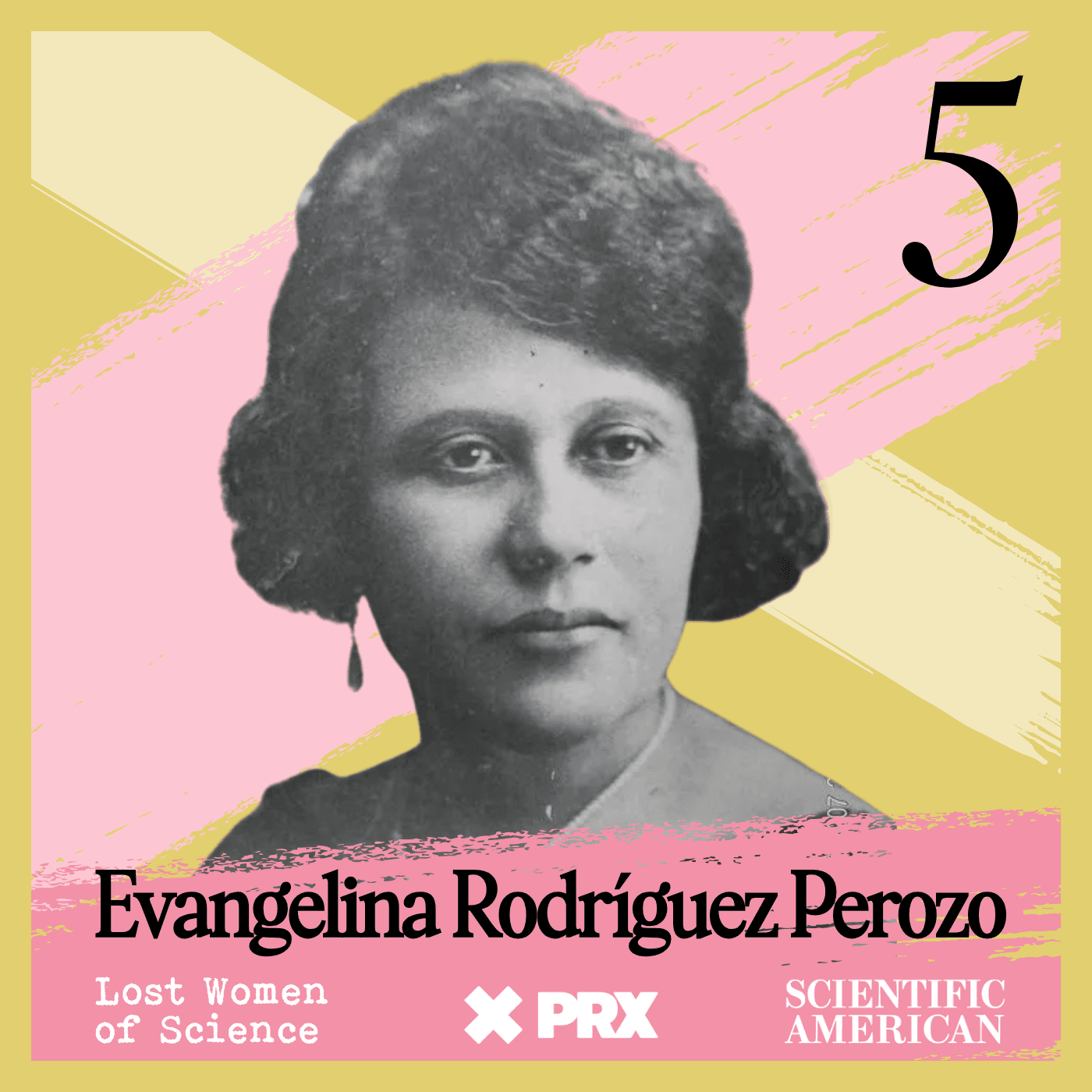
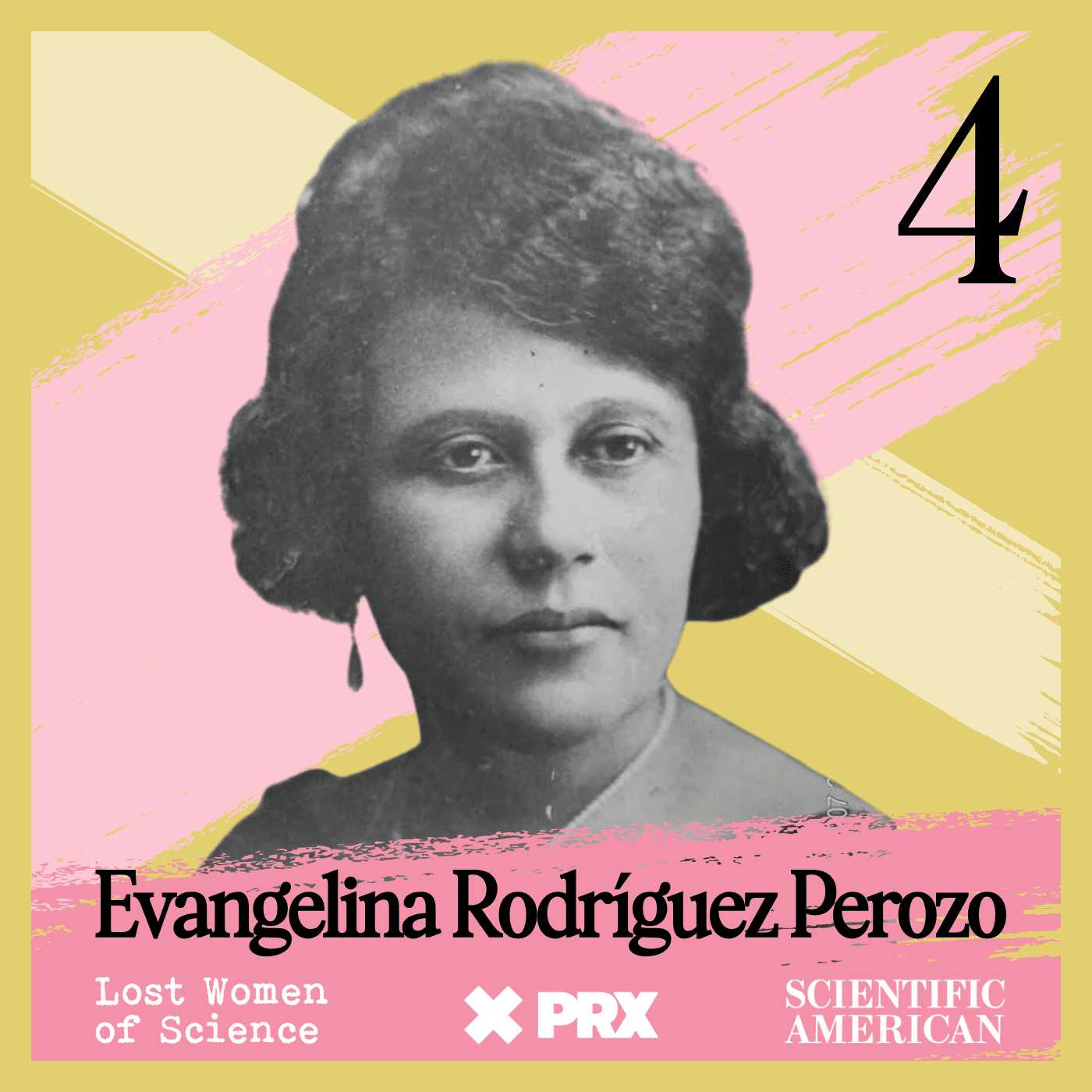
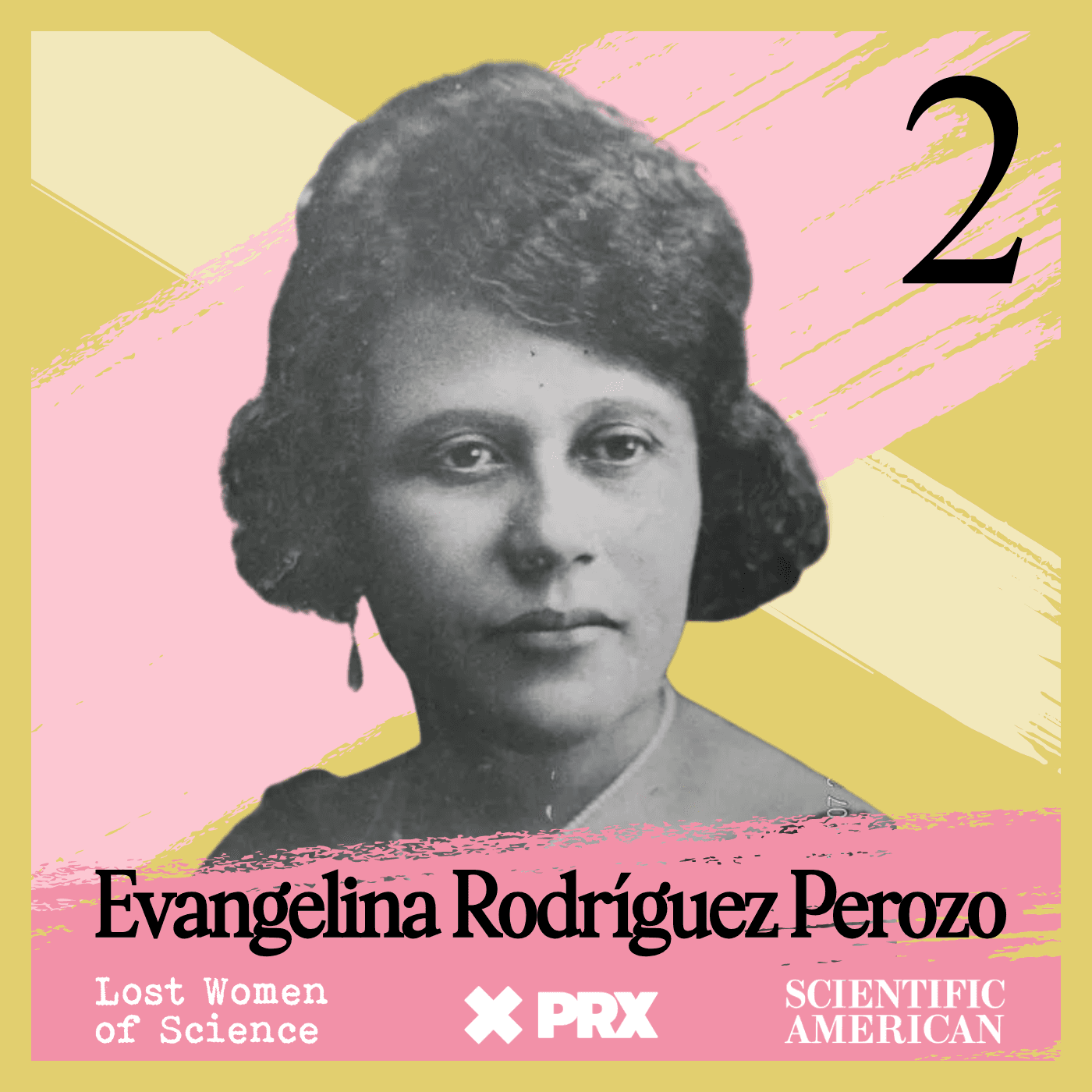
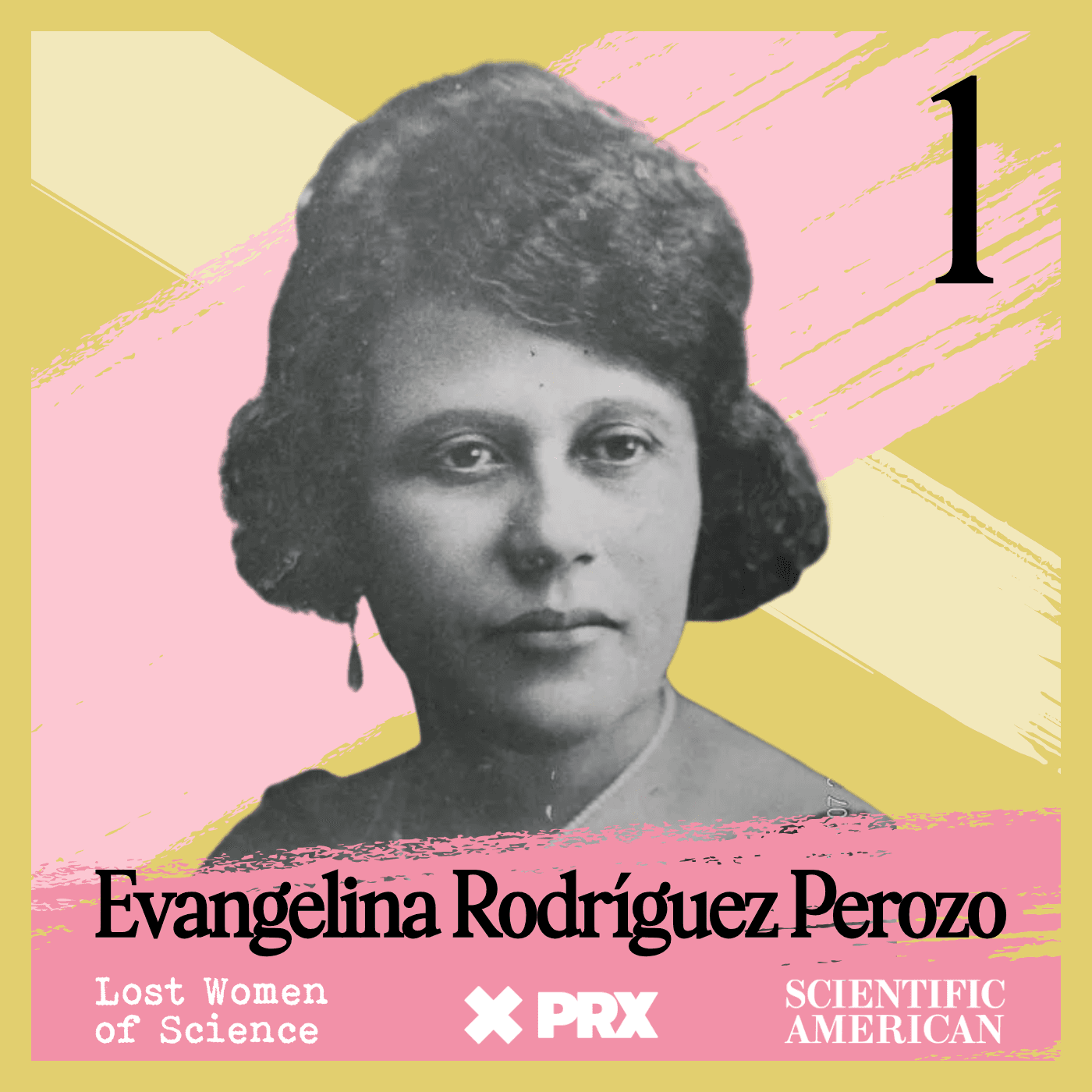
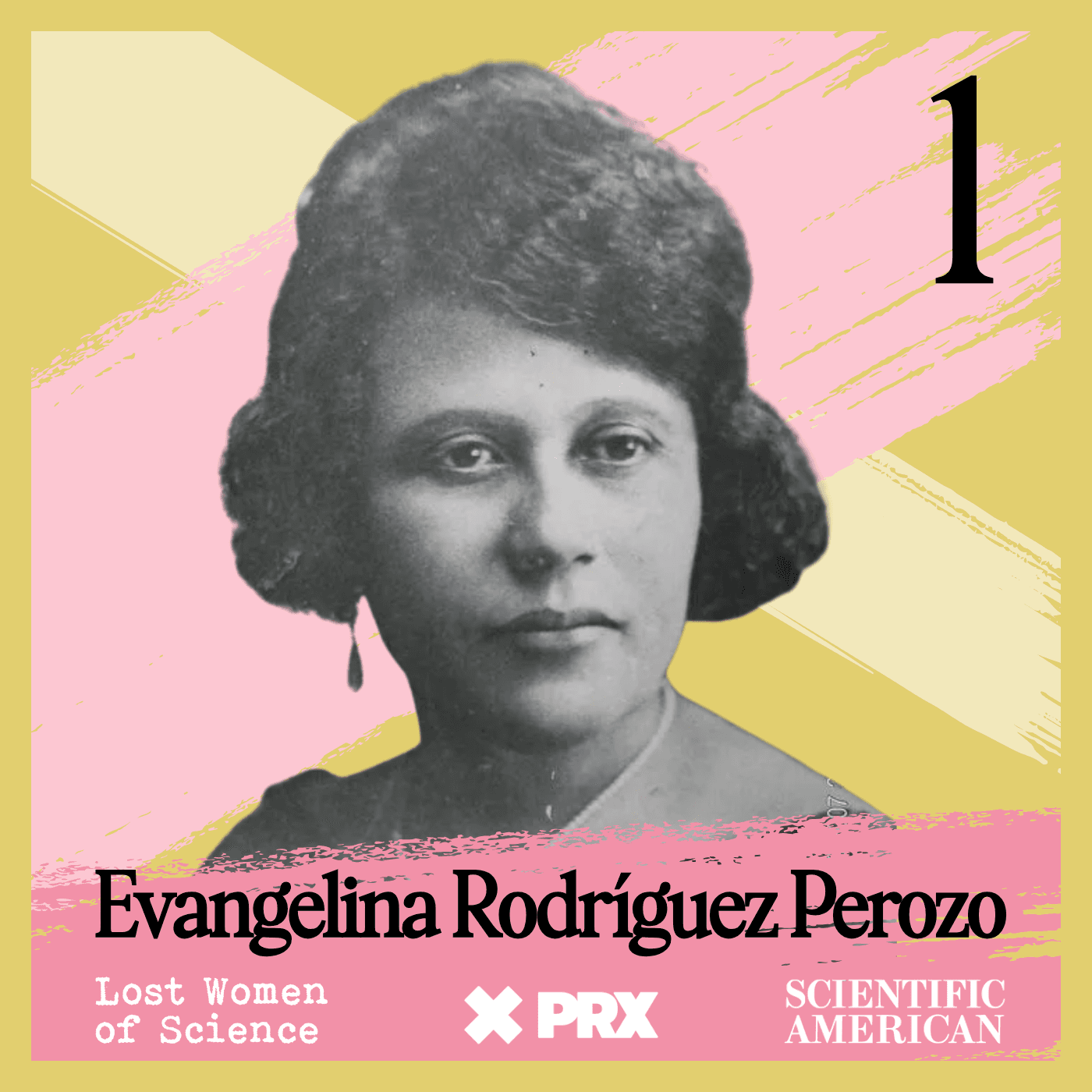
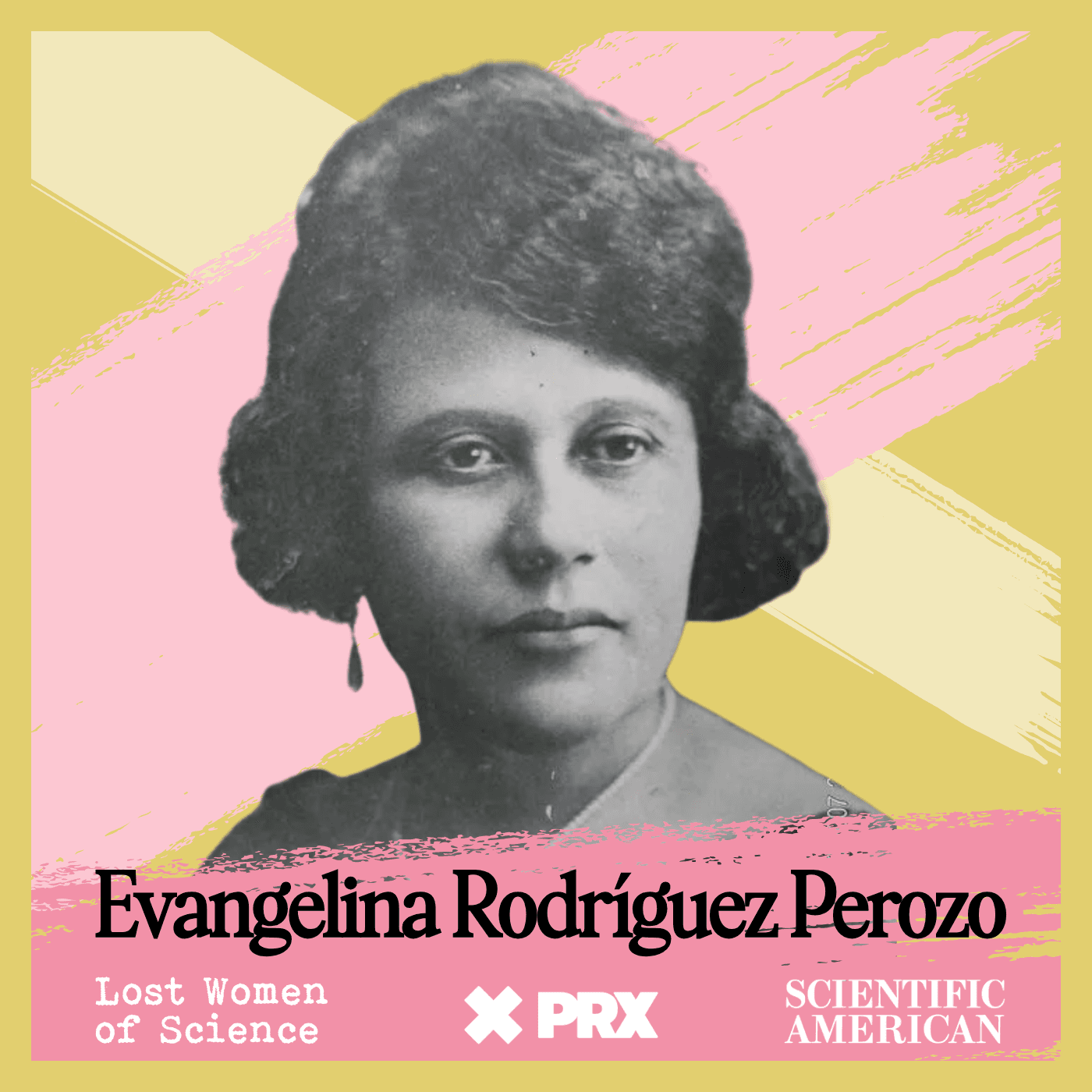
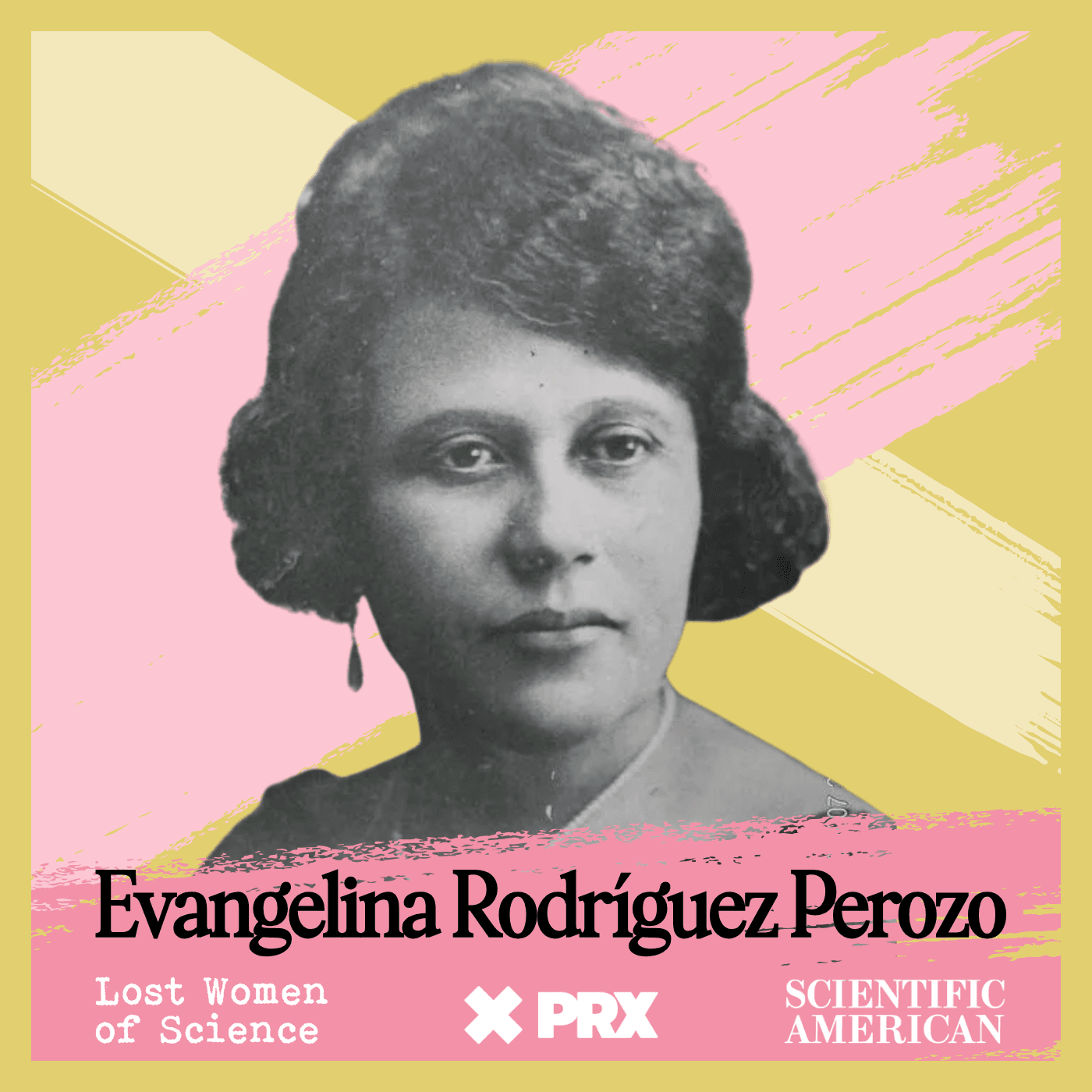







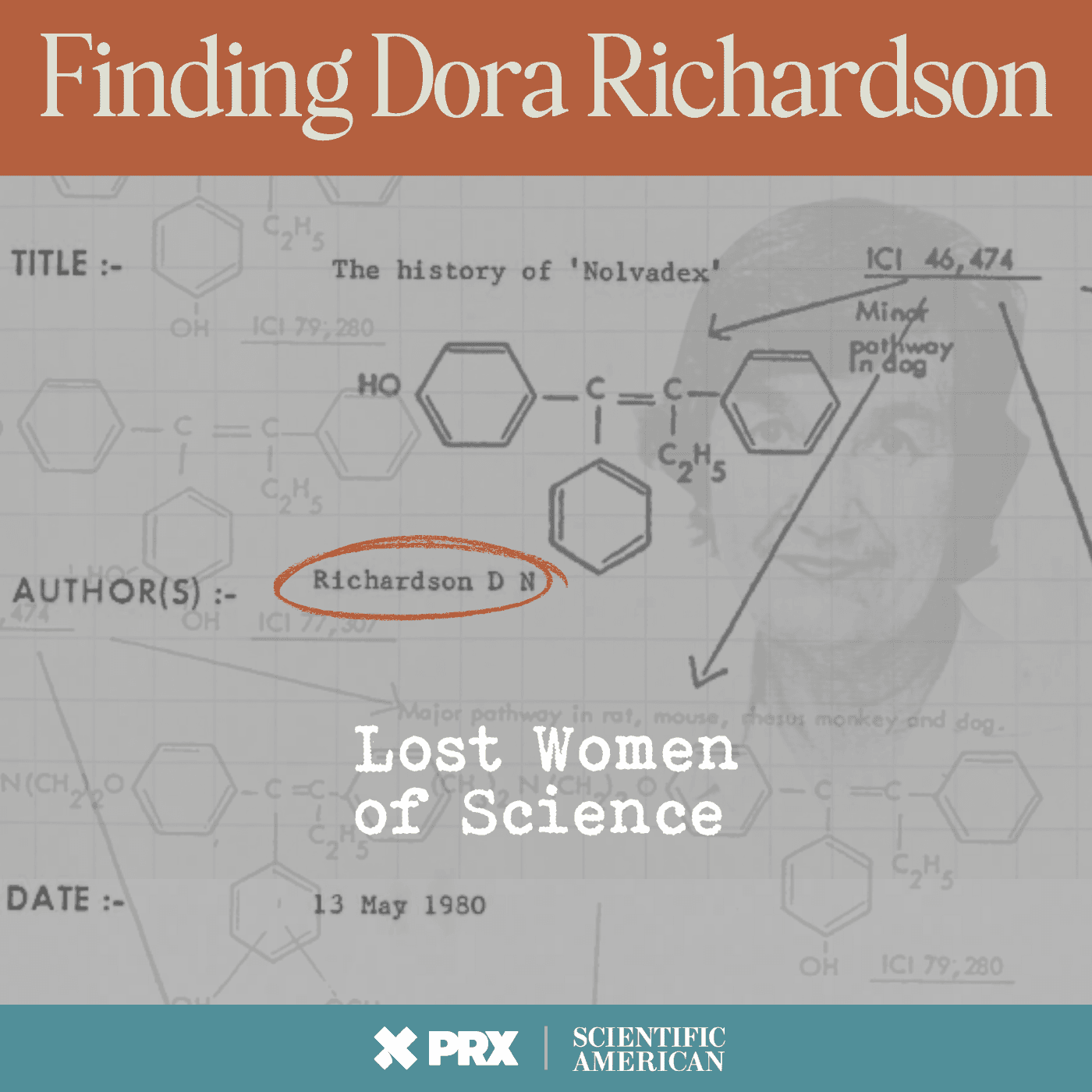
























































What's in a Street Name? Everything.

In 1992, a Dutch doctor named Josh von Soer Clemm von Hohenberg wrote a letter to Henning Voscherau, the mayor of Hamburg, Germany, requesting that a street be named after Marie Nyswander.
The doctor had never met Marie, but he had founded a clinic for treating people with drug addiction, and he’d seen methadone treatment — co-developed by Marie — save lives. Four years later, doctors gathered on a street in northwest Hamburg to celebrate that street’s new name: Nyswanderweg. We’re investigating how German streets get their names, and why so few of them honor women like Marie, who have made historic achievements.
Learn about your ad choices: dovetail.prx.org/ad-choices