
Lost Women of Science
Lost Women of ScienceFor every Marie Curie or Rosalind Franklin whose story has been told, hundreds of female scientists remain unknown to the public at large. In this series, we illuminate the lives and work of a diverse array of groundbreaking scientists who, because of time, place and gender, have gone largely unrecognized. Each season we focus on a different scientist, putting her narrative into context, explaining not just the science but also the social and historical conditions in which she lived and worked. We also bring these stories to the present, painting a full picture of how her work endures.
For every Marie Curie or Rosalind Franklin whose story has been told, hundreds of female scientists remain unknown to the public at large. In this series, we illuminate the lives and work of a diverse array of groundbreaking scientists who, because of time, place and gender, have gone largely unrecognized. Each season we focus on a different scientist, putting her narrative into context, explaining not just the science but also the social and historical conditions in which she lived and worked. We also bring these stories to the present, painting a full picture of how her work endures.
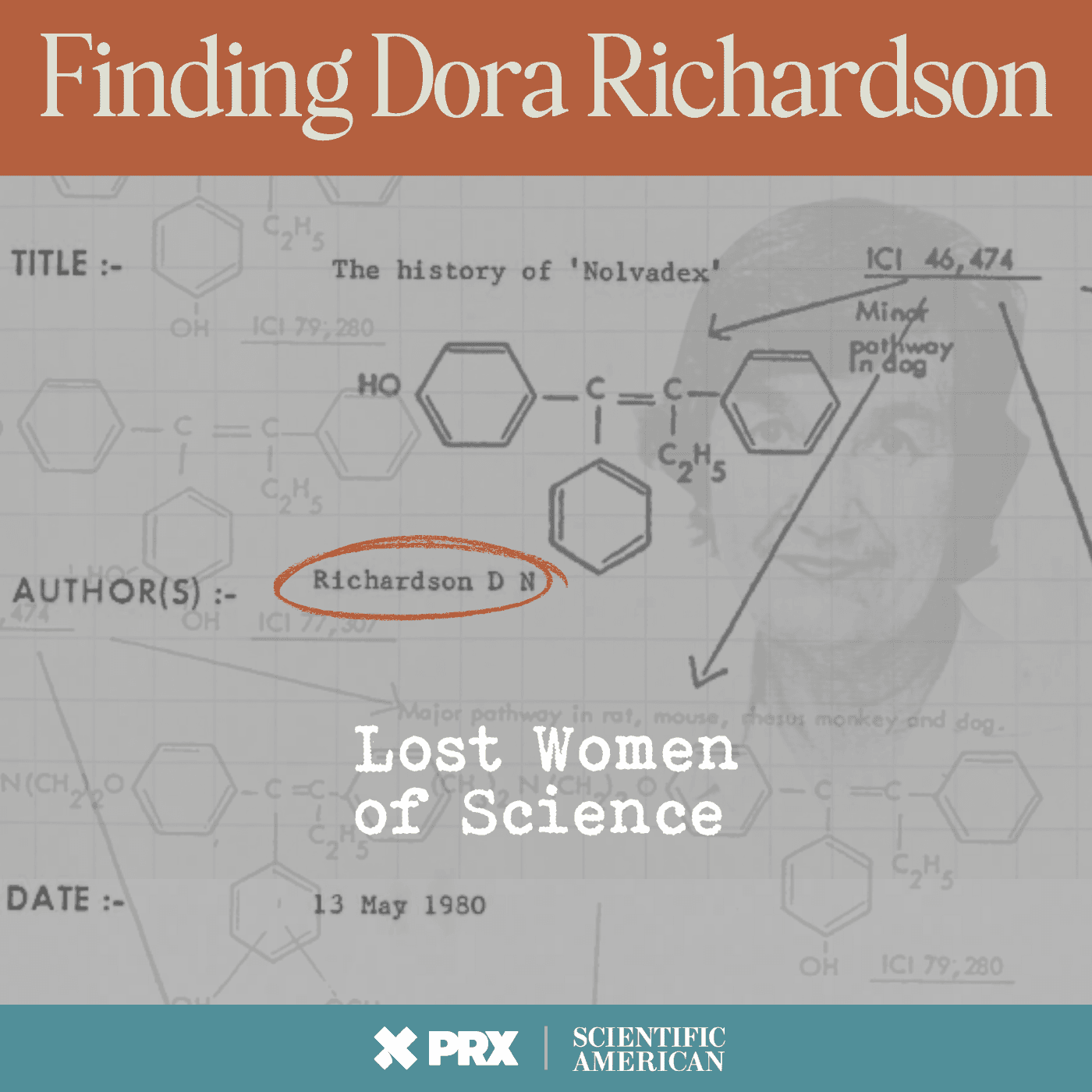





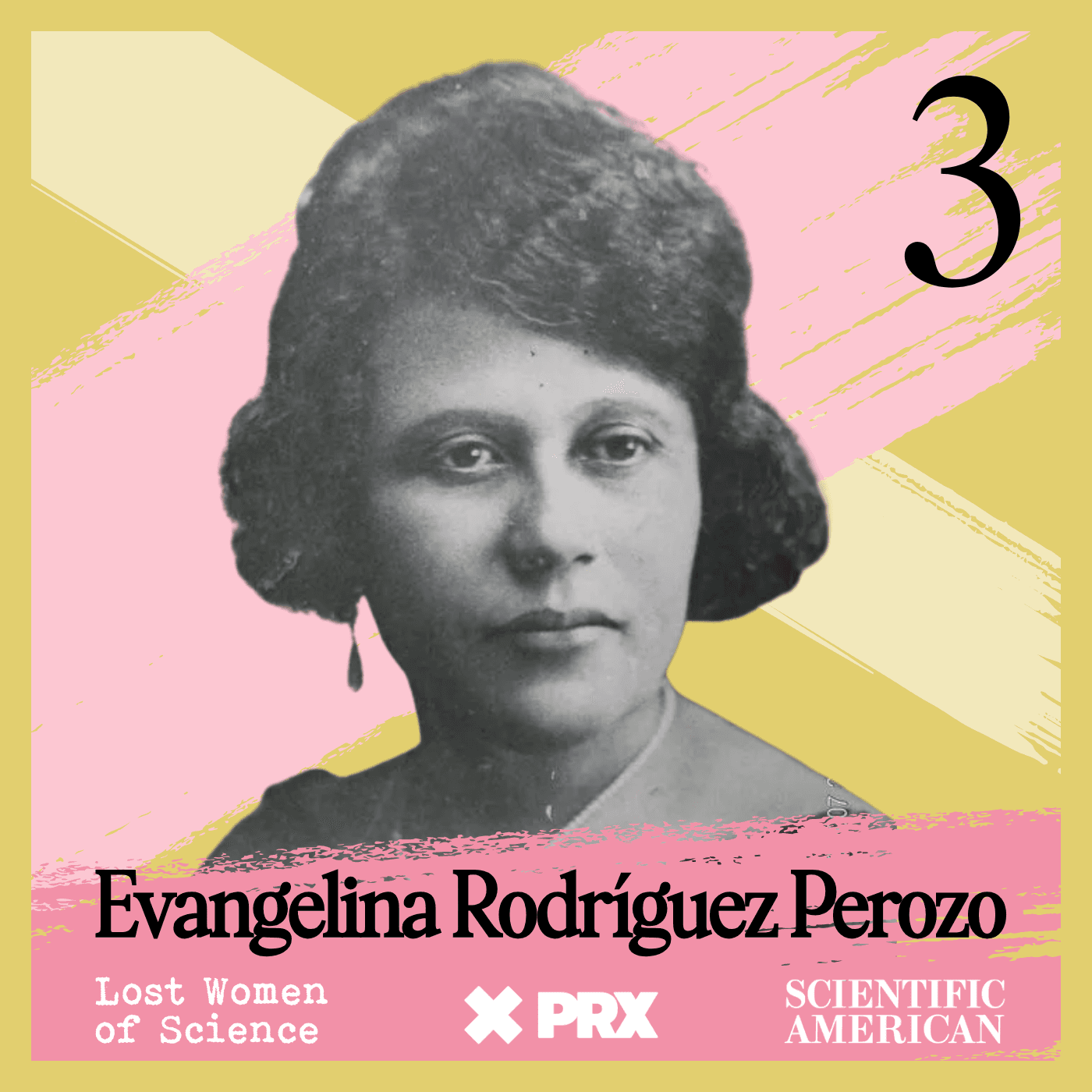
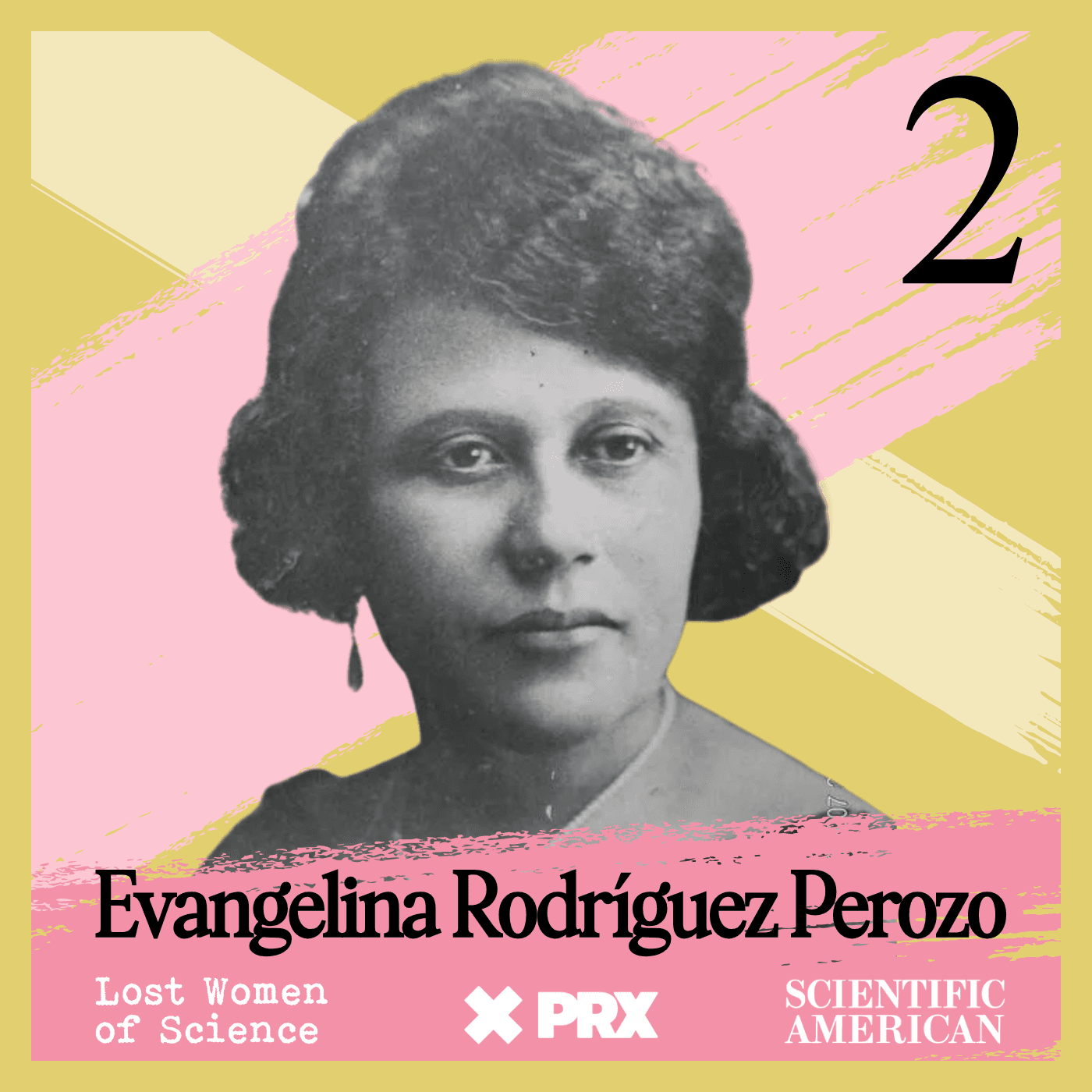
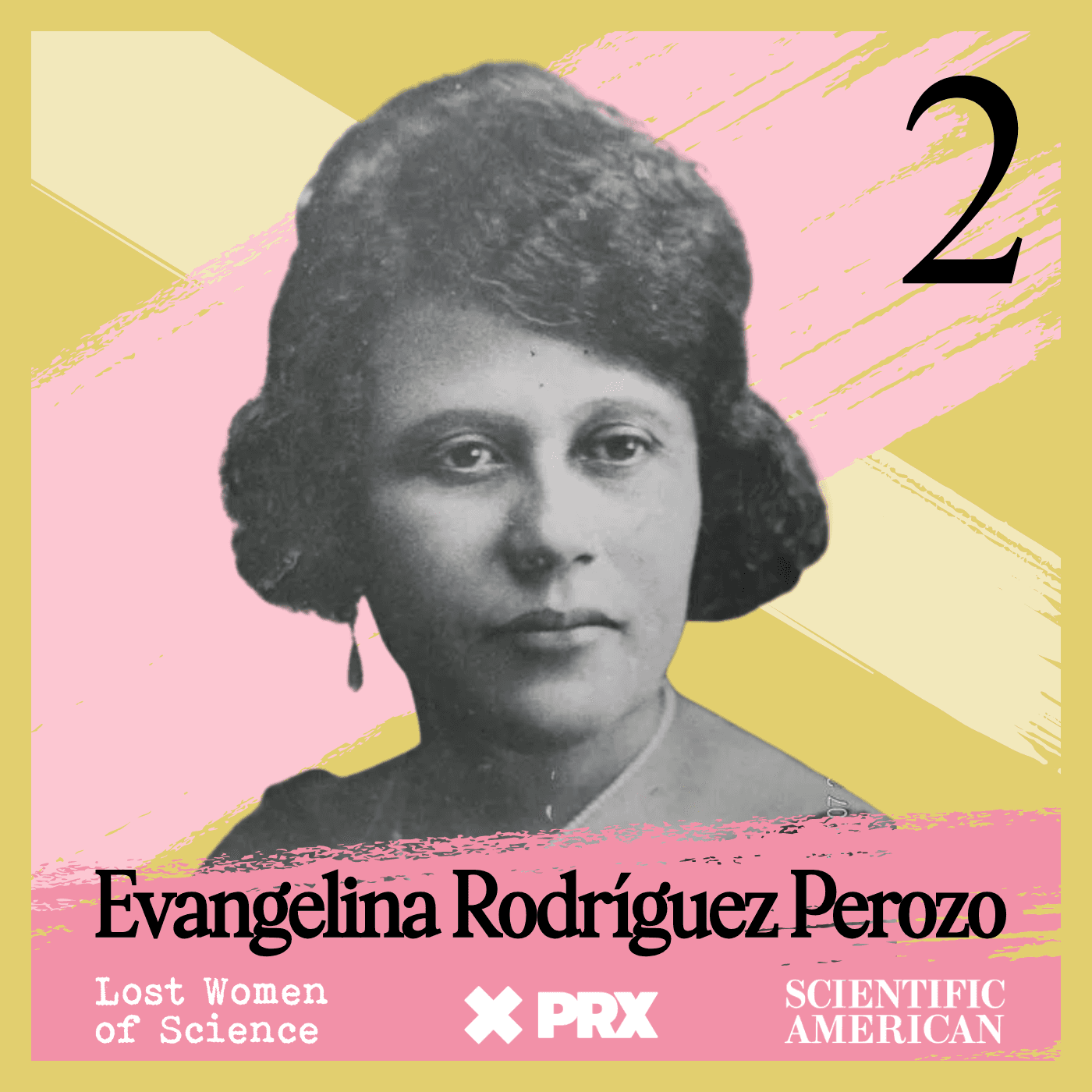
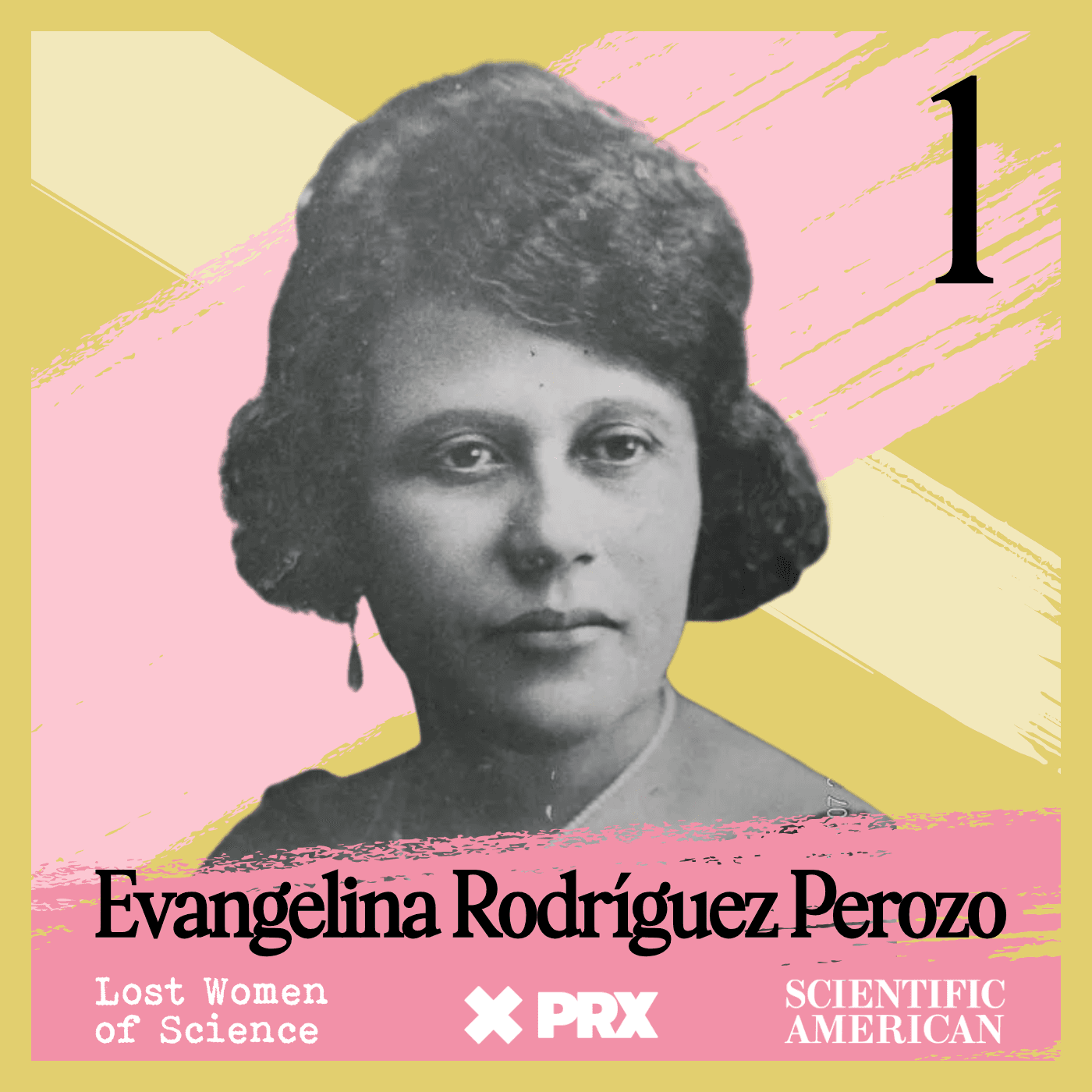
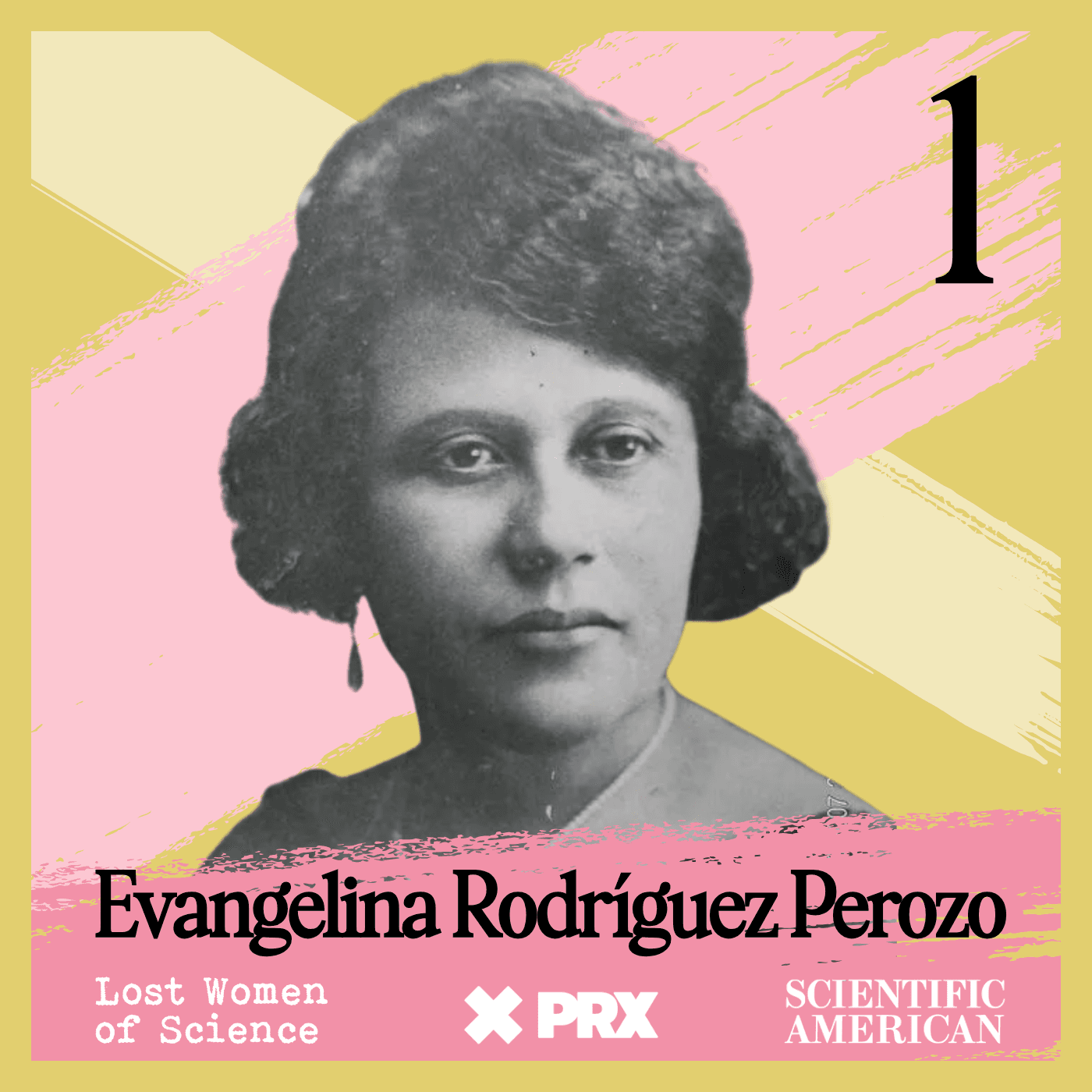































































Finding Dora Richardson - The Forgotten Developer of Tamoxifen

In the early 1960s, chemist Dr. Dora Richardson synthesized a chemical compound that became one of the most important drugs to treat breast cancer: tamoxifen. Although her name is on the original patent, her contributions have been lost to history.
In the first episode of this two-part podcast, Katie Couric introduces us to Dora’s story. Lost Women of Science producer Marcy Thompson tracked down Dora’s firsthand account of the history of the drug’s development. This document, lost for decades, tells the story of how the compound was made and how Imperial Chemical Industries, where Richardson worked, almost terminated the project because the company was hoping to produce a contraceptive, not a cancer therapy.
Learn about your ad choices: dovetail.prx.org/ad-choices